SkyPilot Recipes#
Recipes allow storing, sharing and reusing SkyPilot YAMLs across users. With Recipes, you can:
Reuse patterns across workflows: Create recipes for clusters, managed jobs, pools, and volumes
Launch quickly: Start from a copyable CLI command (e.g.,
sky launch recipes:dev-cluster) - no YAML file requiredEdit in place: View and modify recipes directly in the dashboard
Share templates across your organization: Customize your YAMLs once, then share institutional setup across your team
Getting started#
Recipes are managed through the SkyPilot dashboard. To access Recipes:
Run
sky dashboardNavigate to the Recipes section in the navbar
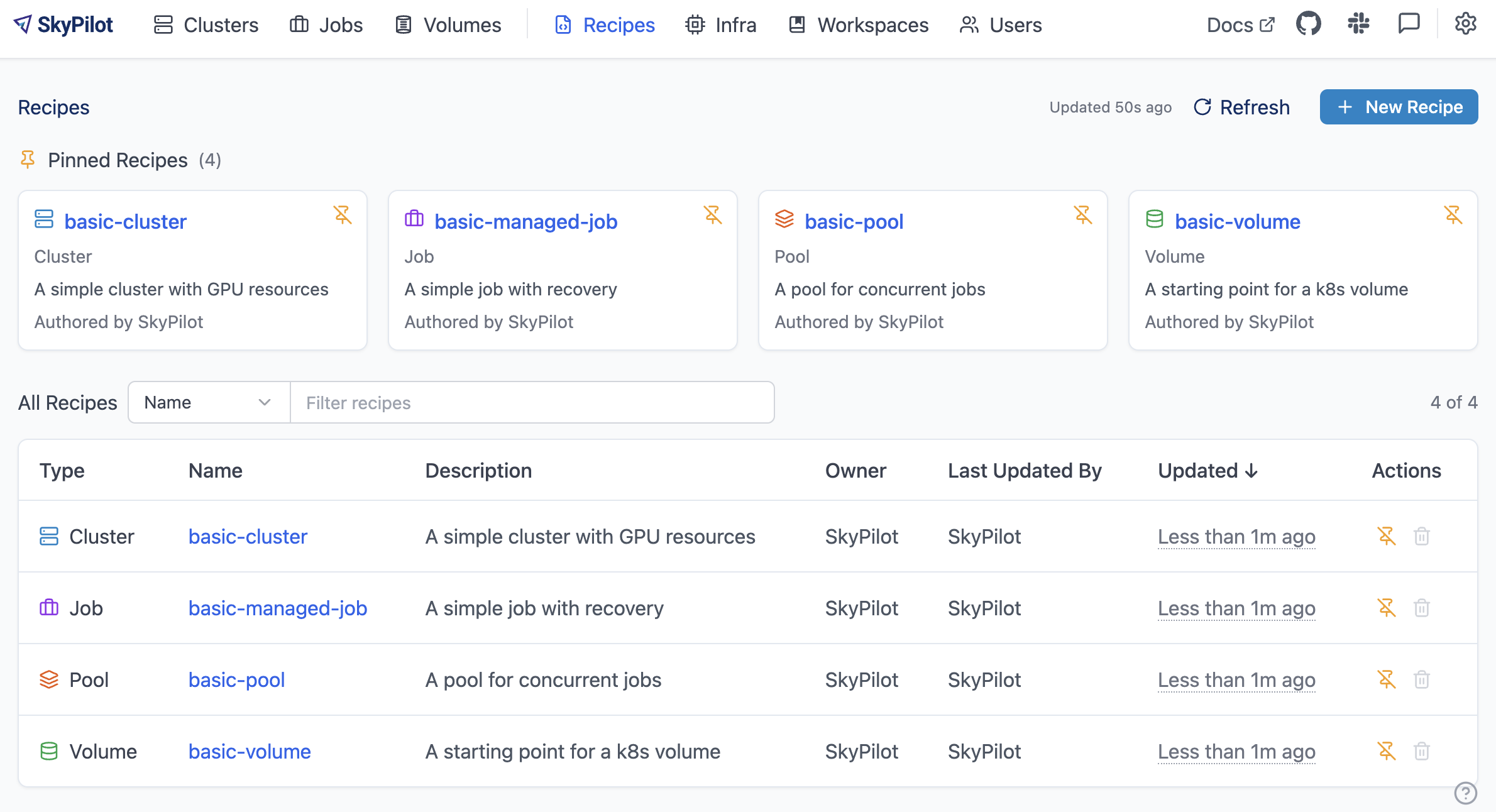
Recipes support these SkyPilot resource types: Clusters, Managed Jobs, Pools, and Volumes.
Creating a recipe#
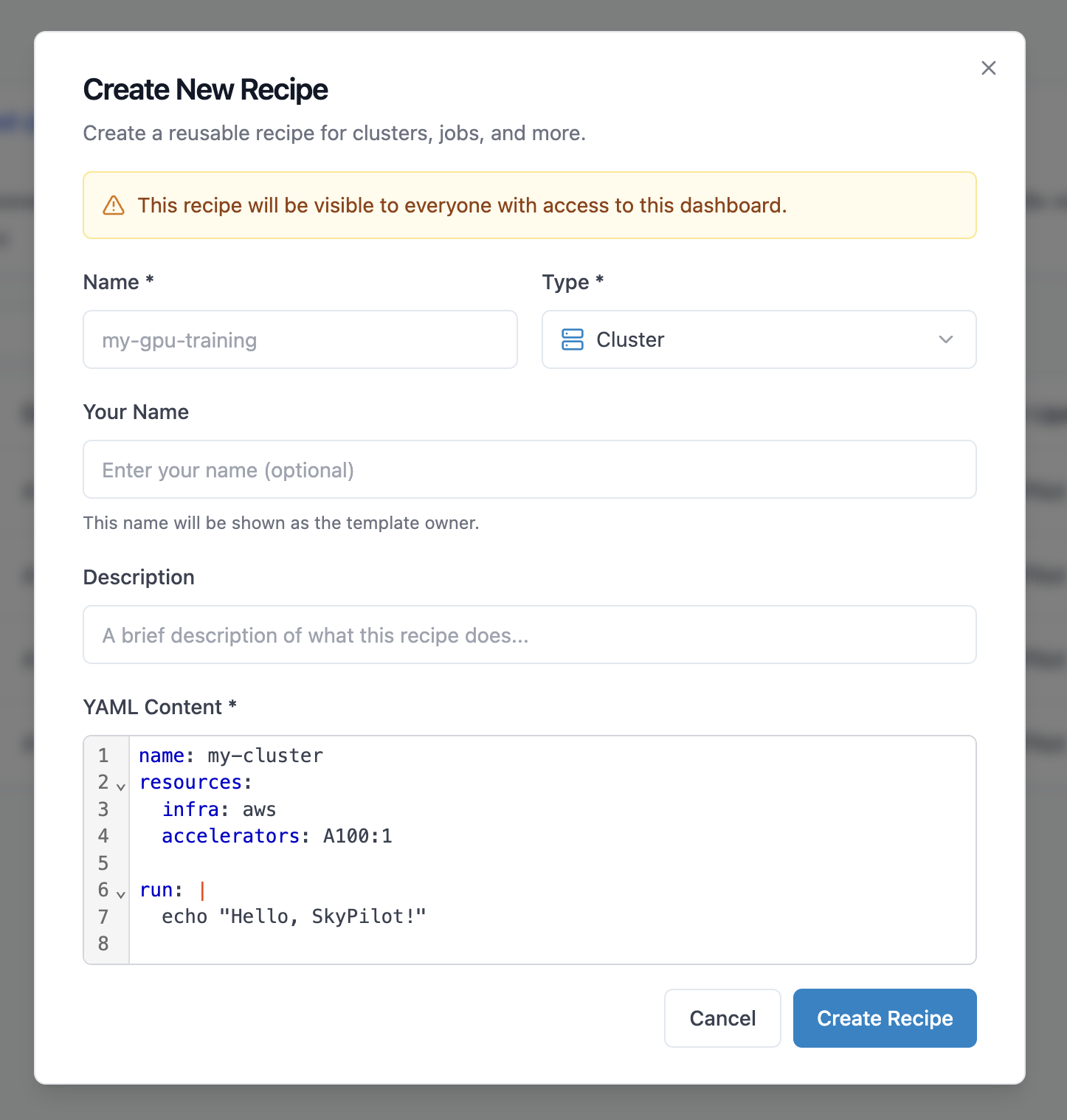
To create a new recipe in the dashboard:
Click New Recipe in the Recipes page
Enter a name and description for your recipe
Select the resource type (cluster, managed job, pool, or volume)
Write or paste your YAML configuration
Click Create Recipe to store the recipe
Note
File and Code Storage Limitations
Recipes do not support local file uploads. For code and data:
Code: Use Git repositories with workdir dictionary format:
workdir: url: https://github.com/org/repo
Data: Use cloud storage buckets with file_mounts (e.g.,
s3://bucket,gs://bucket) or volumes for persistent storageLocal paths (
workdir: .,file_mounts: ~/local-dir) are not supported
Copying from an Existing Recipe
To create a recipe based on an existing one:
Open the recipe you want to copy
Click Copy to New
Modify the name, description, and YAML as needed
Click Create Recipe to create the new recipe
This is useful for creating variations of a recipe (e.g., different GPU types or environment versions).
Launching from recipes#
The most convenient way to use recipes is through the CLI with the recipes: prefix:
# Launch a cluster from a recipe
sky launch recipes:dev-cluster
# Launch with custom cluster name
sky launch -c my-dev recipes:dev-cluster
# Launch a managed job from a recipe
sky jobs launch recipes:training-job
No YAML file needed - the configuration is fetched directly from the SkyPilot API server!
You can override the recipe fields with CLI args:
# Launch with overrides
sky launch recipes:gpu-cluster --cpus 16 --gpus H100:4 --env DATA_PATH=s3://my-data --secret HF_TOKEN
Tip
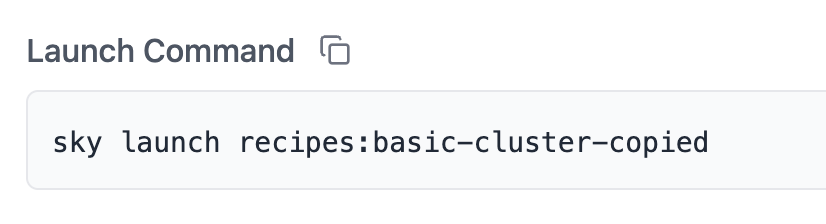
You can find the launch command for your recipe in the dashboard:
Managing recipes#
All recipes are listed in the Recipes page of the dashboard. Click on any recipe to view its details:
YAML Configuration: The full task specification
Launch Command: Copy-paste command to launch the recipe
Metadata: Name, description, type, creator, and update time
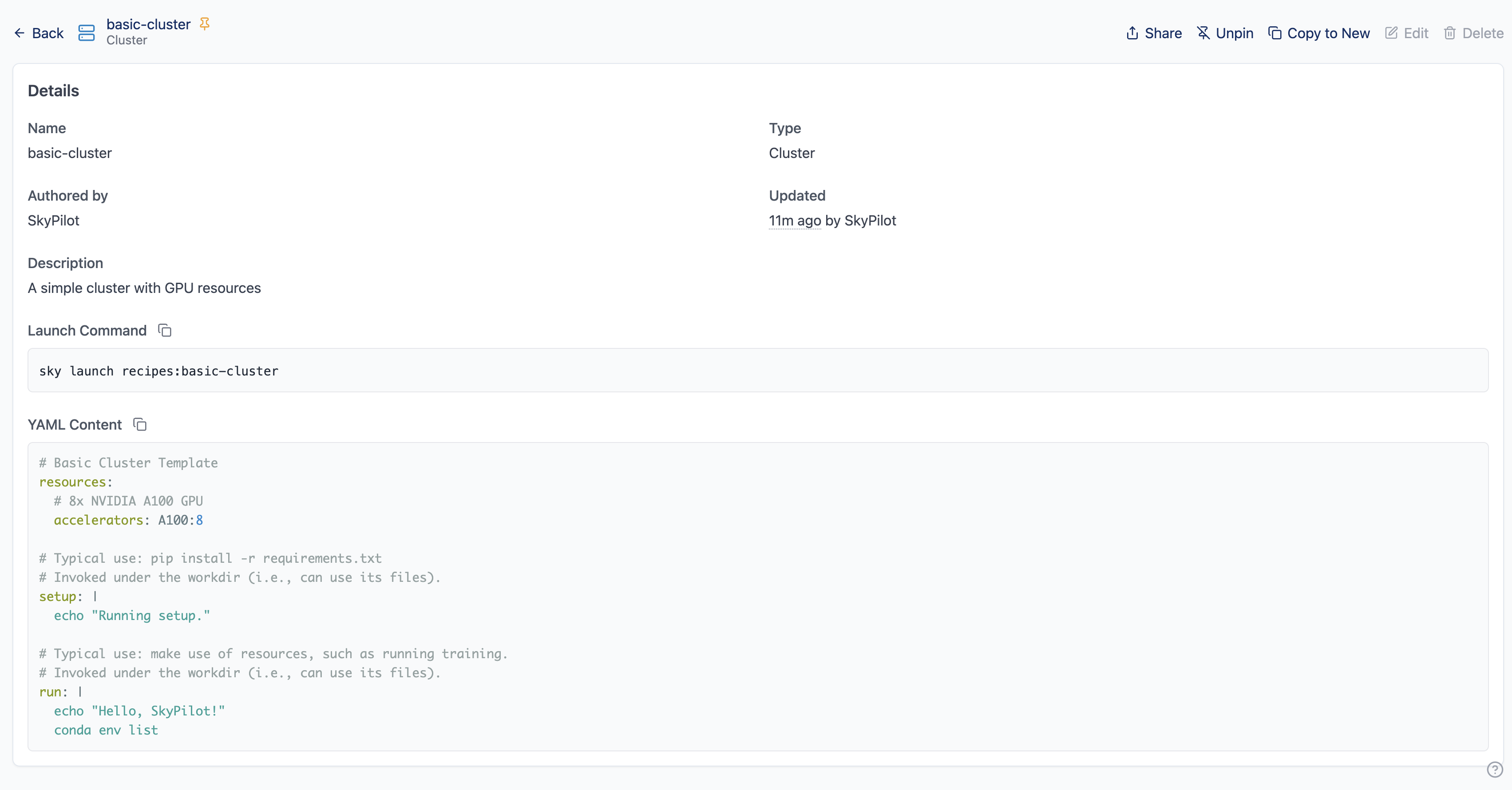
To edit a recipe, open it and click Edit, then update the YAML, name, or description. Changes are saved immediately and available to all users.
To delete a recipe, open it and click Delete, then confirm. Note that deleting a recipe is permanent and cannot be undone. Existing clusters or jobs launched from the recipe will continue running.
Best practices#
Naming: Use clear, descriptive names like dev-cluster-python311, training-a100-8gpu-pytorch, or inference-server-vllm. Avoid generic names like test or recipe1. Include environment or version information when relevant (prod-inference-v2, staging-training).
Documentation: Always include a description explaining what the recipe is for, when to use it, who the intended user is, and any special requirements. Example: “GPU training cluster with PyTorch 2.0 and 8x A100 GPUs. Use for large model training. Requires S3 data bucket configured. Costs ~$20/hour.”
Configuration tips:
Use environment variables for flexibility:
run: | python train.py --data $DATA_PATH --epochs $EPOCHS
Then customize at launch:
sky launch recipes:training --env DATA_PATH=s3://my-dataUse secrets for sensitive values like API keys — they work like environment variables but are redacted in the dashboard:
secrets: HF_TOKEN: null WANDB_API_KEY: null run: | huggingface-cli login --token $HF_TOKEN python train.py
Then pass secrets at launch:
sky launch recipes:training --secret HF_TOKEN --secret WANDB_API_KEYSeparate
setup(one-time installation) fromrun(actual workload) for reusability