Deploy SkyPilot on existing machines#
SkyPilot supports bringing your existing machines, whether they are on-premises or reserved instances on a cloud provider.
Given a list of IPs and SSH credentials, use sky ssh up to turn
them into a SSH Node Pool. It becomes an infra choice on which you can
launch clusters, jobs, or services, just like a regular cloud provider.
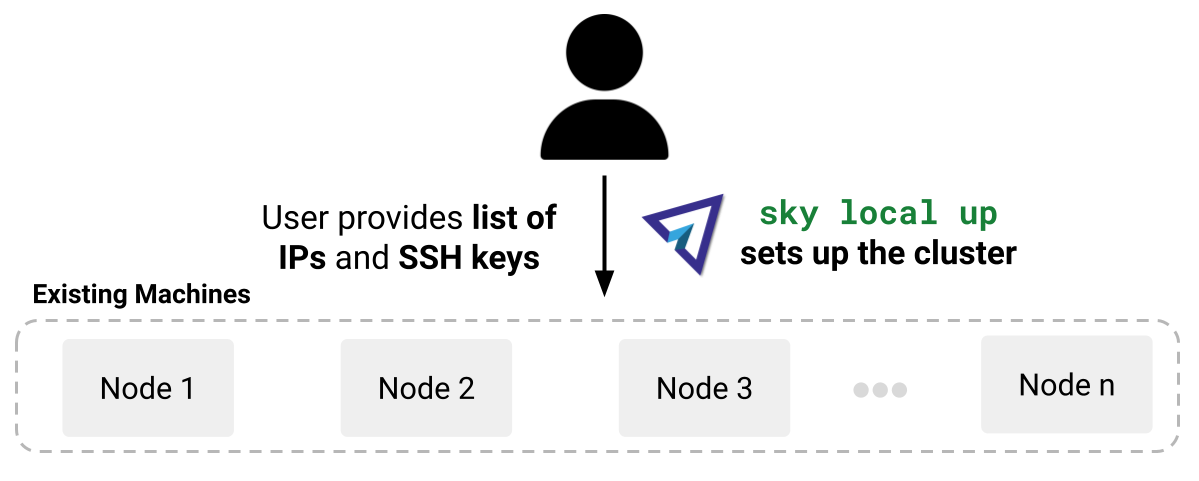
Given a list of IP addresses and SSH keys, sky ssh up will install necessary dependencies on the remote machines and configure SkyPilot to run jobs and services on the cluster.#
Given a list of IP addresses and SSH keys, sky ssh up will install necessary dependencies on the remote machines and configure SkyPilot to run jobs and services on the cluster.#
Quickstart#
Write to ~/.sky/ssh_node_pools.yaml on the host of your API server (refer to Defining SSH Node Pools if you are running a remote API server):
# ~/.sky/ssh_node_pools.yaml
my-cluster: # Give the pool a name.
hosts:
- 1.2.3.4 # Ensure `ssh 1.2.3.4` works.
- 1.2.3.5
my-box:
hosts:
- hostname_in_ssh_config # Ensure `ssh hostname_in_ssh_config` works.
Run sky ssh up to deploy SkyPilot on the machines:
$ sky ssh up
Check that the SSH Node Pools are set up :
$ sky check ssh
...
🎉 Enabled infra 🎉
SSH [compute]
SSH Node Pools:
├── my-cluster
└── my-box
Enabled SSH Node Pools are listed in sky status:
$ sky status
Enabled Infra: ssh/my-cluster, ssh/my-box, ...
...
Launch compute on enabled SSH Node Pools, using --infra ssh/<node_pool_name>:
$ sky launch --infra ssh/my-cluster --gpus H100:1 -- nvidia-smi
$ sky launch --infra ssh/my-box -- echo "Hello, world!"
Equivalently, use resources.infra: ssh/<node_pool_name> in a task YAML:
resources:
infra: ssh/my-cluster
See more customization options and details about SSH Node Pools in the rest of this guide.
Defining SSH Node Pools#
In ~/.sky/ssh_node_pools.yaml, you can define multiple SSH Node Pools, each with a list of IPs and SSH credentials.
If passwordless SSH is enabled, you can simply list the IPs or hostnames:
# ~/.sky/ssh_node_pools.yaml
my-cluster:
hosts:
- 1.2.3.4
- another-node
Alternatively, you can customize SSH options, including:
SSH user
SSH private key
SSH password (if passwordless sudo is not enabled)
Example:
# ~/.sky/ssh_node_pools.yaml
my-cluster:
# Defaults for all nodes in this pool (optional).
user: root
identity_file: ~/.ssh/id_rsa
password: # Optional; if passwordless sudo is not enabled.
# Override defaults for a specific node.
hosts:
- ip: 1.2.3.4
user: alice
identity_file: alice-key
password: alice-password
- ip: 5.6.7.8
user: bob
identity_file: bob-key
password: bob-password
Apply ~/.sky/sky_node_pools.yaml to the API server by the following steps for different setup:
If you did not start an API server instance or use a local API server, set ~/.sky/ssh_node_pools.yaml on your local machine.
If you use a Helm Deployment, follow the SSH Node Pool configuration instructions to upload your ~/.sky/ssh_node_pools.yaml and SSH keys to the API server.
If you use a VM Deployment, set ~/.sky/ssh_node_pools.yaml on the API server host.
This is usually only available to the administrator who deployed the API server.
If any SSH key is needed, you should also set it on the API server host.
Observability of SSH Node Pools#
Open sky dashboard and click on the Infra tab to see an overview of all SSH Node Pools:
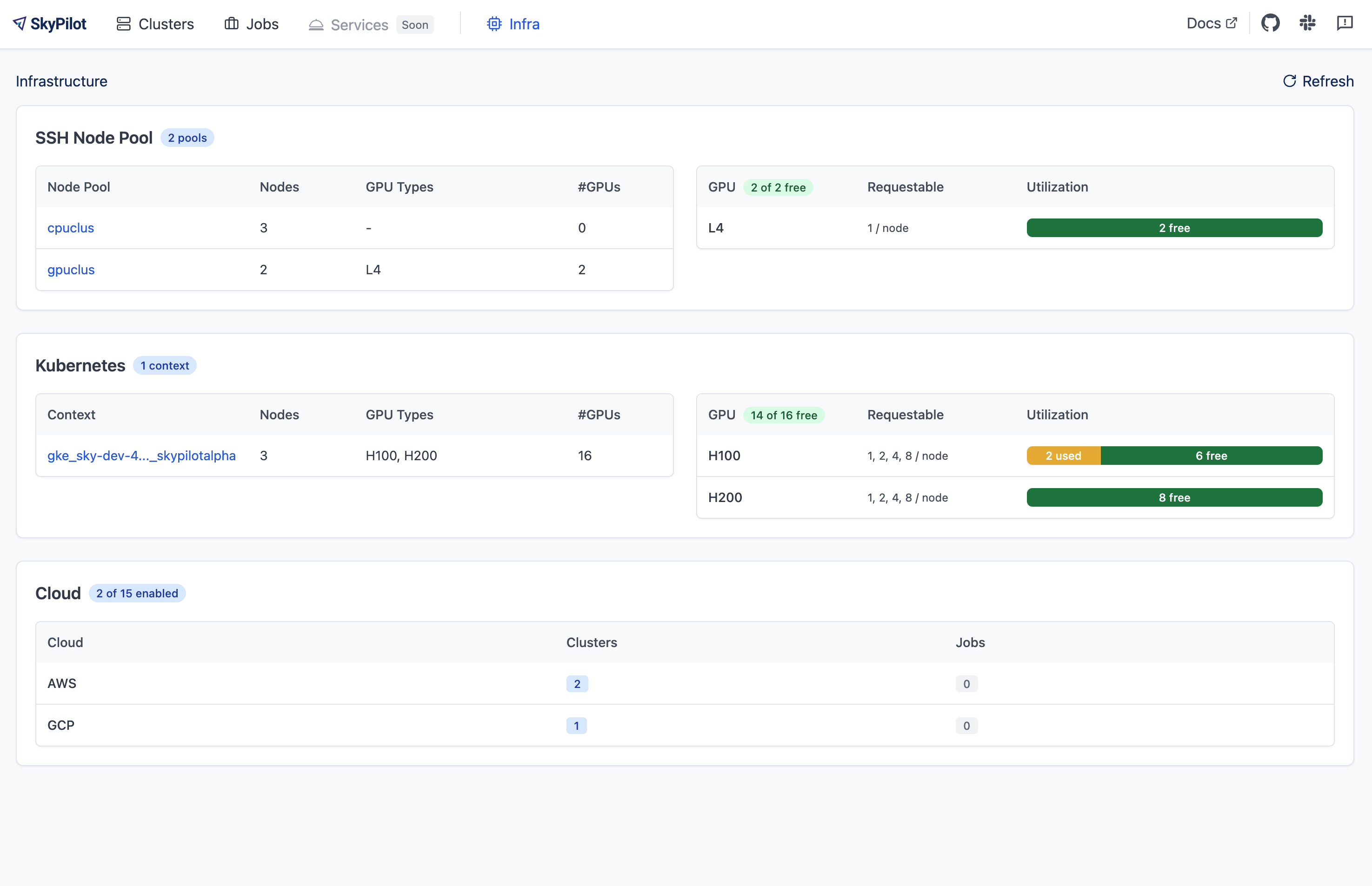
Click on an SSH Node Pool to see more details, including per-node GPU availability:
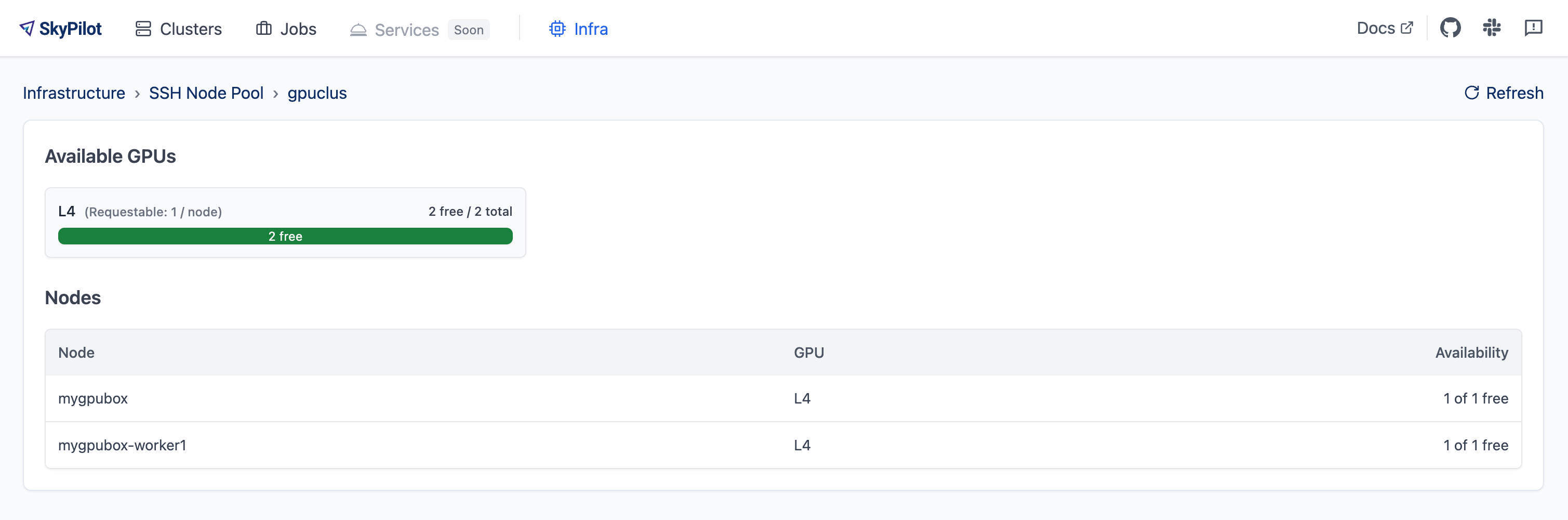
To use the CLI to see what GPUs are available, run:
$ sky show-gpus --infra ssh
$ sky show-gpus --infra ssh/my-cluster
Using multiple SSH Node Pools#
You can set up multiple SSH Node Pools as shown above.
Once set up, you can launch compute on either a specific SSH Node Pool, or let SkyPilot automatically select one with available resources.
# Run on cluster1
sky launch --infra ssh/cluster1 -- echo "Running on cluster 1"
# Run on cluster2
sky launch --infra ssh/cluster2 -- echo "Running on cluster 2"
# Let SkyPilot automatically select the cluster with available resources.
sky launch --infra ssh -- echo "Running on SkyPilot selected cluster"
Attaching NFS and other volumes#
SkyPilot jobs can access NFS, shared disks, or local high-performance storage like NVMe drives available on your host machines in a SSH Node Pool.
Volume mounting can be done directly in the task YAML on a per-task basis, or globally for all tasks in ~/.sky/config.yaml.
Any path available on the host can be directly mounted to SkyPilot jobs. For example, to mount a NFS share available on the hosts:
Per-task configuration:
# task.yaml
run: |
echo "Hello, world!" > /mnt/nfs/hello.txt
ls -la /mnt/nfs
config:
ssh:
pod_config:
spec:
containers:
- volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /mnt/nfs
name: my-host-nfs
volumes:
- name: my-host-nfs
hostPath:
path: /path/on/host/nfs
type: Directory
Global configuration:
# ~/.sky/config.yaml
ssh:
pod_config:
spec:
containers:
- volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /mnt/nfs
name: my-host-nfs
volumes:
- name: my-host-nfs
hostPath:
path: /path/on/host/nfs
type: Directory
SSH Node Pools running on Nebius VMs can access Nebius shared filesystems.
When creating a VM on the Nebius console, attach your desired shared file system to the VM (Create virtual machine -> Attach shared filesystem):
Ensure
Auto mountis enabled.Note the
Mount tag(e.g.filesystem-d0).
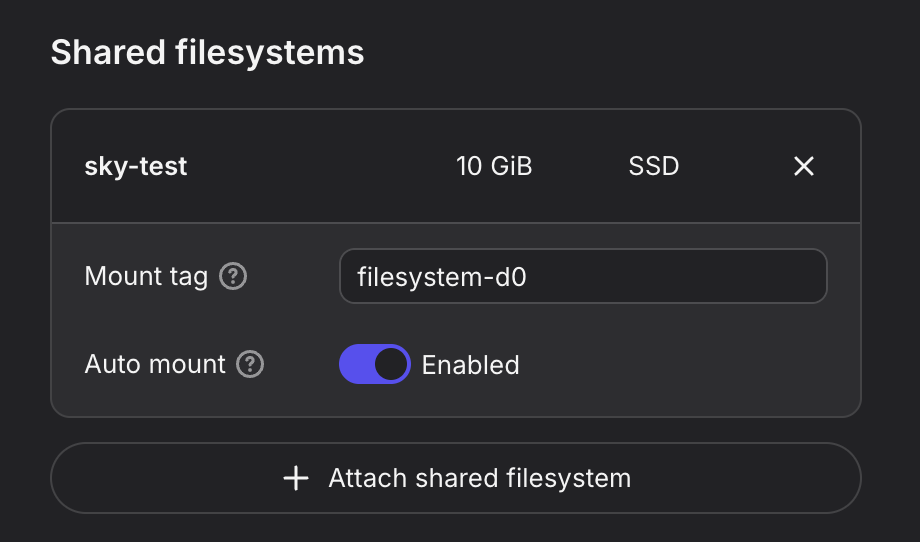
Nebius will automatically mount the shared filesystem to all hosts. You can then attach the volume to your SkyPilot jobs:
Per-task configuration:
# task.yaml
run: |
echo "Hello, world!" > /mnt/nfs/hello.txt
ls -la /mnt/nfs
config:
ssh:
pod_config:
spec:
containers:
- volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /mnt/nfs
name: nebius-sharedfs
volumes:
- name: nebius-sharedfs
hostPath:
path: /mnt/<mount_tag> # e.g. /mnt/filesystem-d0
type: Directory
Global configuration:
# ~/.sky/config.yaml
ssh:
pod_config:
spec:
containers:
- volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /mnt/nfs
name: nebius-sharedfs
volumes:
- name: nebius-sharedfs
hostPath:
path: /mnt/<mount_tag> # e.g. /mnt/filesystem-d0
type: Directory
Cleanup#
To remove all state created by SkyPilot on your machines, run sky ssh down.
$ sky ssh down
This removes the SkyPilot runtime on your machines and disables the SSH Node Pools.
Details: Prerequisites#
SkyPilot API server host:
Remote machines:
Debian-based OS (tested on Debian 11).
SSH access from SkyPilot API server host to all remote machines.
All nodes within a SSH Node Pool must have access to port 6443 to its peers (e.g., same VPC). Port 6443 doesn’t have to be open to machines outside of the network.
Nodes should not be part of an existing Kubernetes cluster (use Kubernetes Support instead).
When working with GPU instances, GPU drivers must be installed on the host. Verify by running
nvidia-smi.